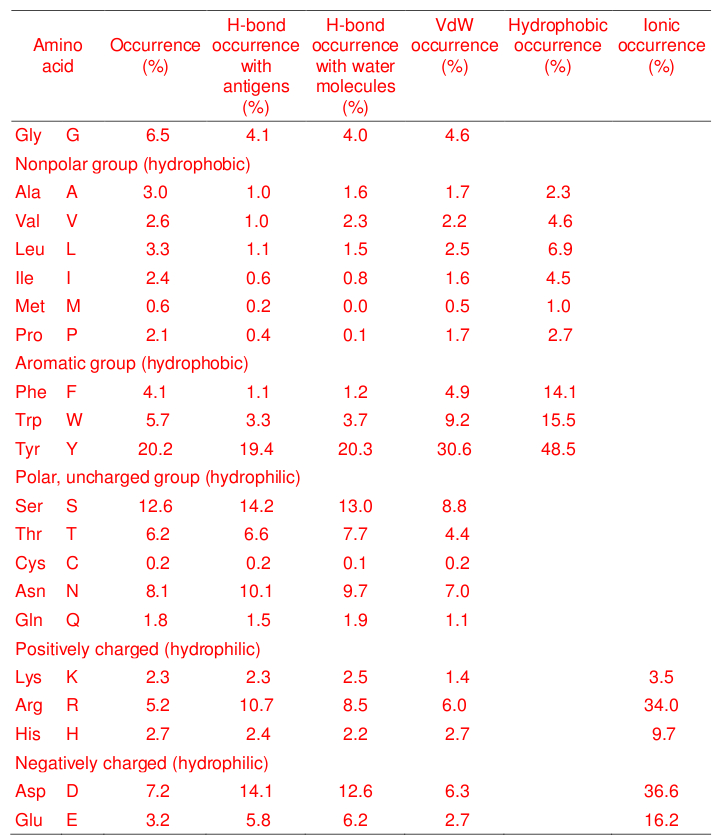
A major effort towards developing tools for antibody engineering has been focused on understanding the physico-chemical characteristics of the paratope and epitope regions. The paratope is the most important region of an antibody for recognition of the epitope of its antigen with specificity and high affinity. Previous studies have shown that antibody paratopes are enriched with aromatic amino acids (Kringelum et al., 2013; Ramaraj et al., 2012). Despite these studies , a comprehensive analysis of the interactions of the contact atoms and residues of antibody structures with antigen surfaces in terms of hydrogen bonds, hydrophobic, van der Waals, and ionic interactions has not been reported. We now build upon the earlier studies by analyzing these interactions from a more comprehensive and larger dataset (403 antibody-antigen complexes) consisting of 8603 contact residues.
Our study confirms that Tyr plays an especially important role in interactions with
epitopes of structurally diverse antigens (Davies and Cohen, 1996; Kringelum et al.,
2013; Mian et al., 1991; Ramaraj et al., 2012) as it has the highest frequency of
participation in epitope binding as well as the highest number of hydrogen bonds,
hydrophobic, and van der Waals interactions. The aromatic residue Trp and the short-
chain hydrophilic residue Ser are enriched in the contact residues of antibody structures
as has also been observed previously in studies of the available smaller datasets
(Kringelum et al., 2013; Ramaraj et al., 2012). However, our analysis has revealed that
additionally, Gly has a significantly high number of hydrogen bonds and van der Waals
interactions in the contact residues of antibody structures even though Gly does not
have a sidechain. Although this has not previously been reported, nevertheless,
Fellouse et al., in designing an antibody library, concluded that Gly in CDR-H3 is
important for providing a conformation suitable for high-affinity binding (Fellouse et al.,
2007). In addition to Gly, our study suggests that Asn, Asp, Thr, Arg contribute
substantially to epitope binding. Recently, Chen et al. reported the construction of an
antibody library and found that antibody-antigen interaction specificity is enhanced by
incorporating short-chain hydrophilic residues (Asn, Asp, Thr, and Ser) in CDRs (Chen
et al., 2015).
|