

Comparison of RNA 3D Structures
|
 |
|
 |
|
 |
|
 |
|
 |
|
 |
|
 |
Query structure
The whole structure 2vpl The structure 2vpl, chain B The structure 2vpl, chains B and D The query in this case would be a 2 fragment structure constituting residues 2-17 and 29-49 of the structure 2vpl, chain B.
Note:The user uploaded structures cannot be fragments like the chosen PDB structures. The user uploaded structures should be pre-fragmented (if so desired).Choice of representative atomRoot Mean Square DeviationGiven two RNA structures A and B, root mean square deviation (RMSD) is the norm of the distance vector between the two sets of coordinates of representative atoms, after superimposition. It is given by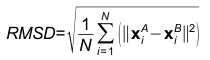
Structure OverlapStructure overlap (also called equivalent positions) is defined as the percentage of the representative atoms (C3' for RNA structures, and C3' and Cα for RNA-protein complexes) in the structure A that are within 4Å (RMSD cut-off) of the corresponding atoms in the superimposed structure B.Match SizeMatch size (also called absolute similarity) is defined as the number of atoms in the list of equivalence.Heutistics in structure alignmentsHeurisitics are applied to ensure local chain connectivity. Chain connectivity is broken when equivalent residues are not contiguous in sequence. The equivalent residue matches before the application of heuristics is shown in the output file linked to "Matched residue pairs".Rules:
Fragment ScoreOn applying heuristic measures to maintain chain or fragment continuity, some residue matches are eliminated from consideration, as they do not belong to (or are in the close proximity of) contiguously matched fragments. The fragment score is the ratio of the number of matched positions in the alignment before and after the application of heuristics. This is a handy measure to estimate the extent of similarity between two structures. The fragment score is close to 1 (the maximum value) for similar structures.Topology ScoreThe topology score is a measure of how similar the topologies of the matched structures are to one another. It is computed based on the directionality of the matched sequence fragments. Topology score varies between a maximum of 1 for topologically identical structures and 0 for those are the topologically completely dissimilar.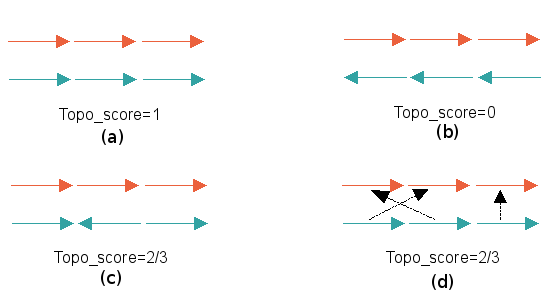
In each of the 4 examples, the two structures that are matched consist of 3 different sequence segments. The direction of the arrows that symbolize each segment show the direction from N to C termini. Unless explicitly indicated with black arrows, the segments in the top structure is aligned to one that it is directly above. 4 different cases of sequence alignments implied by Rclick structural alignment are illustrated here a) The sequence alignment maintain topology; topology score = 1. b) The directionality from N To C of the sequence on top is the exact opposite of that to the one in the bottom; topology score = 0. c) Two of the three sequence segments have the same directionality; topology score = 0.66. d) Two of the 3 segments are matched but not in sequential order; topology score = 0.66 |